gukbi
jdbc 사용 해보기
sqlplus system/oracle@//localhost:1521
create user c##human identified by human;
grant connect,resource,dba to c##human;
conn c##human/human@//localhost:1521
-- 1. 다음 human table sql를 c##human/human 계정에 만들어 보자.
drop table human;
create table human(
name nvarchar2(30),
age number(3),
height number(7,3),
birthday date
);
insert into human(name,age,height,birthday)
values('김수호',20,160.4,to_date('2005:05:05 02:25:50','YYYY:MM:DD HH24:MI:SS'));
insert into human(name,age,height,birthday)
values('나수호',24,170.8,to_date('2000:10:15 12:25:10','YYYY:MM:DD HH24:MI:SS'));
insert into human(name,age,height,birthday)
values('박수호',27,188.6,to_date('1995:12:04 13:45:14','YYYY:MM:DD HH24:MI:SS'));
commit; -- 반드시 커밋을 해야 한다.
select * from human;
package com.human.ex;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class JdbcTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn=null;
String sql=null;
Statement st=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
String url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:";
String user="c##human";
String pw="human";
conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,pw);
sql="select * from human";
st=conn.createStatement();
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()) {
String name =rs.getString("name");
int age=rs.getInt("age");
double height=rs.getDouble("height");
LocalDateTime birthday=rs.getTimestamp("birthday").toLocalDateTime();
System.out.println("name:"+rs.getString(1));
System.out.println("age:"+rs.getInt(2));
System.out.println("height:"+rs.getDouble(3));
System.out.println("birth:"+rs.getTimestamp(4));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(rs!=null)rs.close();
if(st!=null) st.close();
if(conn!=null) conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
package com.human.ex;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class JdbcSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
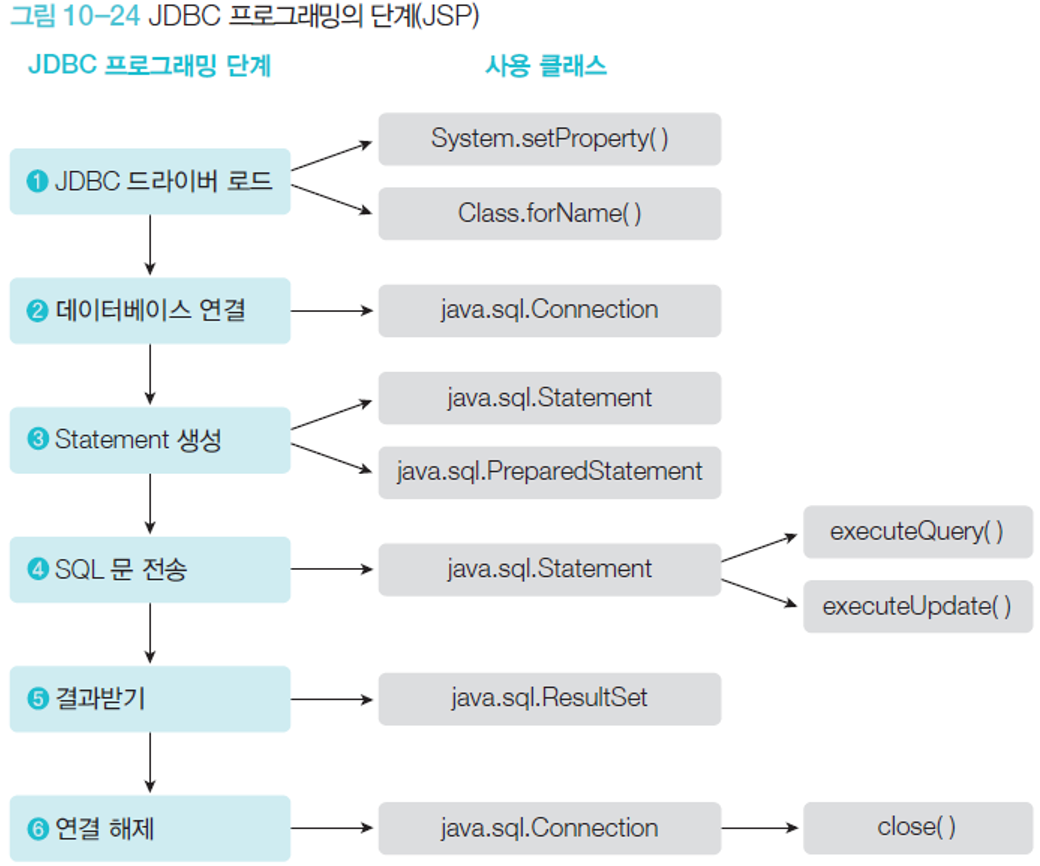
//1. 드라이버 로딩
//class.forName == new 클래스() 문자열로 클래스 생성하는 메소드
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 연결");
//2. 데이터베이스 연결 Connection 클래스
//jdbc:oracle:thin:(제품명)@localhost(주소):1521(포트):xe(씨드아이디)
String url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:";
String user="c##human";
String pw="human";
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,pw);
System.out.println("데이터베이스에 접속 성공");
//3. 데이터베이스 sql문 전송을위한 쿼리 생성과 담당 객체 생성(statement)
String sql="select * from human";
System.out.println(“sql 에러시 여기서 문자열을 확인:”+sql);
Statement st=conn.createStatement();
//4. 데이터베이스에 sql문을 전송
ResultSet rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
//5. resultSet출력하기
//ResultSet rs 에 sql문 실행 결과가 테이블 형태로 담겨져 있다.
// 읽어올때 사용하는 메소드
//.getInt() .getDouble() .getString() .getTimestamp()
// 읽어 올때 여러 컬럼중 어떤 컬럼의 값을 가져올 것인가?
//2가지 방법이 있는데
//1. 테이블 만들때 기술한 순서의 숫자
//2. 테이블 만들때 사용한 컬럼명으로 읽어오는 방법
while(rs.next()) {
//1. 테이블 만들때 기술한 순서의 숫자
// String name =rs.getString(1);
// int age=rs.getInt(2);
// double height=rs.getDouble(3);
// LocalDateTime birthday=rs.getTimestamp(4).toLocalDateTime();
// System.out.println("name:"+name);
// System.out.println("age:"+age);
// System.out.println("height:"+height);
// System.out.println("birth:"+birthday);
// System.out.println("---------------------------");
//2. 테이블 만들때 사용한 컬럼명으로 읽어오는 방법
String name =rs.getString("name");
int age=rs.getInt("age");
double height=rs.getDouble("height");
LocalDateTime birthday=rs.getTimestamp("birthday").toLocalDateTime();
System.out.println("name:"+name);
System.out.println("age:"+age);
System.out.println("height:"+height);
System.out.println("birth:"+birthday);
System.out.println("---------------------------");
}
//6. 데이터베이스와 연결된 자원을 반납
if(rs!=null) rs.close();
if(st!=null) st.close();
if(conn!=null) conn.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
st.executeQuery(); // 리턴값이 있다.
st.executeUpdate(); // 리턴값이 없다.